ACH payments are a cornerstone of modern finance that enables businesses and individuals to transfer funds electronically through the Automated Clearing House network. This comprehensive guide explores what ACH payments are, how they function, their benefits for financial management, and how to effectively track and optimize your ACH payment processes for maximum efficiency and security.
1. What Is an ACH Payment?
An ACH payment is an electronic, bank-to-bank money transfer processed through the Automated Clearing House (ACH) Network. Governed by Nacha (formerly the National Automated Clearing House Association), this network facilitates payments within the United States. Instead of using paper checks, wire transfers, or credit cards, ACH payments move funds directly between bank accounts electronically. This method is widely used for various transactions, whether completed online or originating from processes related to in-store activities.
For businesses processing numerous transactions like payroll, vendor payments, or customer debits, understanding and utilizing the ACH payment network is crucial for efficiency, cost savings, and maintaining financial oversight. Individuals commonly encounter ACH payments through direct deposit of salaries or automatic bill payments. The ACH network handles billions of electronic financial transactions annually, making it essential to understand how these payments flow through the system.
2. The Complete ACH Payment Process
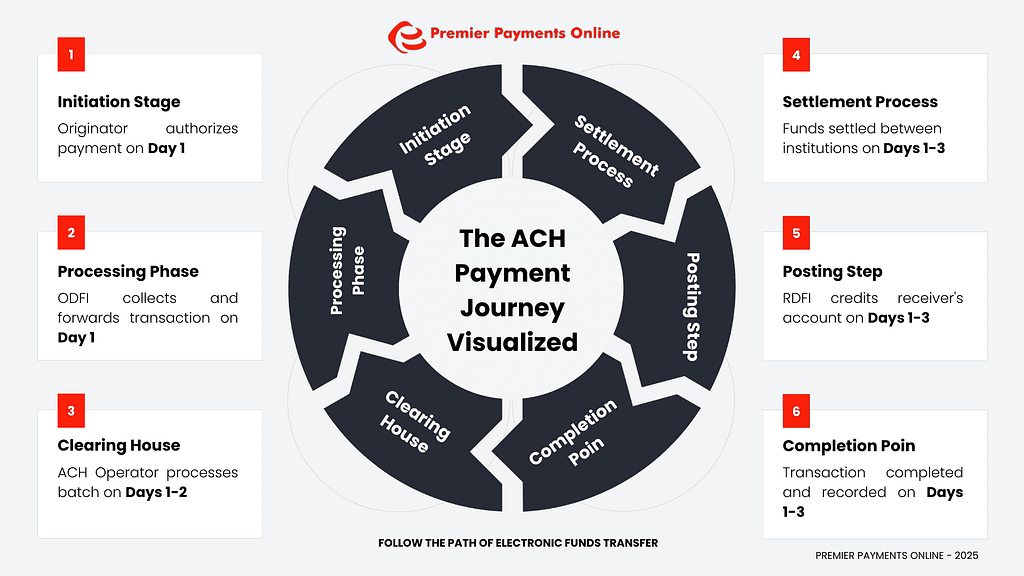
The ACH payment process involves several key steps as funds move from the originator to the receiver:
| Stage | Description | Timeframe |
| Initiation | The originator (payer or payee initiating a debit) authorizes and initiates an ACH payment transaction. | Day 1 |
| Processing | The Originating Depository Financial Institution (ODFI – the originator’s bank) collects the transaction and forwards it in a batch to an ACH Operator. | Day 1 |
| Clearing | The ACH Operator (either the Federal Reserve or The Clearing House) sorts the batches and makes transactions available to the Receiving Depository Financial Institution (RDFI – the receiver’s bank). | Day 1-2 |
| Settlement | Funds are settled between the ODFI and RDFI through their accounts at the Federal Reserve. | Day 1-3 |
| Posting | The RDFI credits or debits the receiver’s account according to the ACH payment instructions. | Day 1-3 |
| Completion | The transaction is completed and recorded by both financial institutions. | Day 1-3 |
Understanding these stages helps businesses track the status of their ACH payments and manage their electronic payment operations effectively.
3. Types of ACH Payments
ACH payment transactions fall into two main categories:
3.1 ACH Credits
ACH credit transactions involve “pushing” funds from the originator’s account to the receiver’s account. The originator initiates the ACH payment.
Common ACH Credit Examples:
| Description | Example |
| Direct Deposits | Salary, wages, reimbursements from employers |
| Tax Refunds | Government payments to taxpayers |
| Vendor Payments | Business-to-business (B2B) payments |
| Interest/Dividend Payments | Financial distributions from investments |
3.2 ACH Debits
ACH debit transactions involve “pulling” funds from the receiver’s account based on prior authorization. The payee (originator) initiates the ACH payment transaction to collect funds.
Common ACH Debit Examples
| Description | Example |
| Recurring Bill Payments | Utilities, subscriptions, loans, and mortgage payments |
| One-time Purchases | E-commerce transactions usingthe bank account |
| Membership Dues | Regular payments to organizations |
| Check Conversion (ARC/POP/BOC) | Converting a paper check to an ACH payment debit |
Understanding the difference between these ACH payment types is crucial for managing payment flows and ensuring proper authorization for debits.
4. Benefits of Using ACH Payments for Business Management
Implementing ACH payments in your financial operations provides several significant advantages:
| Benefit | Description |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Significantly lower transaction fees for ACH payments compared to wire transfers or credit card processing. |
| Efficiency & Automation | Streamlines recurring payments (payroll, subscriptions) and reduces manual processing of checks. |
| Enhanced Tracking | Electronic nature allows for easier monitoring and status updates of ACH payment transactions (often via portals). |
| Improved Reconciliation | Simplifies matching incoming and outgoing ACH payments with bank statements. |
| Predictable Cash Flow | Scheduled ACH payments provide better visibility into the timing of fund availability and debits. |
| Reduced Errors | Minimizes errors associated with manual check processing and data entry for ACH payments. |
| Security | Operates under strict Nacha rules, making ACH payments generally more secure than paper checks. |
| Convenience | Offers convenience for both payers (automation) and payees (direct deposit via ACH payment). |
For businesses processing high volumes of transactions, the combined benefits of ACH payment make it an essential component of modern financial operations.
5. ACH Payment Processing Time
One important aspect of ACH payments is the processing timeline. While not instantaneous like wire transfers, ACH payment processing offers predictable settlement windows. Standard ACH payment processing typically takes 1-3 business days, while Same-Day ACH offers accelerated options.
| ACH Processing Type | Typical Submission Deadline* | Settlement Time |
| Standard ACH | Varies by ODFI | 1-3 business days |
| Same-Day ACH (Window 1) | 10:30 AM ET | ~1:00 PM ET same day |
| Same-Day ACH (Window 2) | 2:45 PM ET | ~5:00 PM ET same day |
| Same-Day ACH (Window 3) | 4:45 PM ET | End of processing day (Fedwire closes 6:30 PM ET) |
Deadlines are set by Nacha; your financial institution may have earlier internal cutoffs for submitting an
Understanding these processing windows is key for managing cash flow and setting expectations for ACH payment completion. You can learn more about general processing timelines by exploring how long payment elections take to process.
6. Setting Up ACH Payment Processing
For businesses looking to implement ACH payments, consider these steps:
6.1 Key Considerations:
- Choose an ACH Provider: Decide whether to work directly with your bank (ODFI) or use a third-party payment processor specializing in ACH payment.
- Understand Nacha Rules: Familiarize yourself with the operating rules and requirements, especially regarding authorization for ACH payment debits.
- Obtain Authorization: For ACH payment debits, you must obtain clear and compliant authorization from the account holder before initiating transactions.
- Integration: Determine how ACH payment processing will integrate with your existing accounting, payroll, or ERP software.
- Security Protocols: Implement strong security measures for handling sensitive bank account information related to ACH payments.

6.2 Implementation:
Setting up ACH payment processing involves establishing a relationship with your chosen provider, configuring software or platforms, ensuring compliance with regulations, and training staff on procedures. Many providers offer platforms or APIs to streamline integration and management of ACH payments.
7. ACH Payment Tools and Software
Several types of tools and software facilitate ACH payment processing and management:
| Tool Type | Features | Best For |
| Bank Platforms | Direct ODFI services, often integrated with business banking accounts. | Businesses with strong bank relationships |
| Third-Party Processors | Specialized ACH payment services, often with APIs, reporting, and risk management tools. | Businesses needing flexibility or specific features |
| Payment Gateways | Offer ACH payment alongside credit card processing, consolidating payment types. | E-commerce, SaaS, and businesses needing multiple methods |
| Accounting Software | Built-in or integrated ACH payment capabilities for payroll, payables, receivables. | Small to mid-sized businesses |
| Custom API Solutions | Direct integration into proprietary software for tailored ACH payment workflows. | Larger enterprises, tech companies |
Premier Payments Online offers robust solutions that combine its ACH & check acceptance program with advanced tracking capabilities, providing comprehensive ACH payment transaction management tools.
8. ACH Payments vs. Other Payment Methods: Comparison
Understanding how ACH payments compare helps businesses choose the right methods:
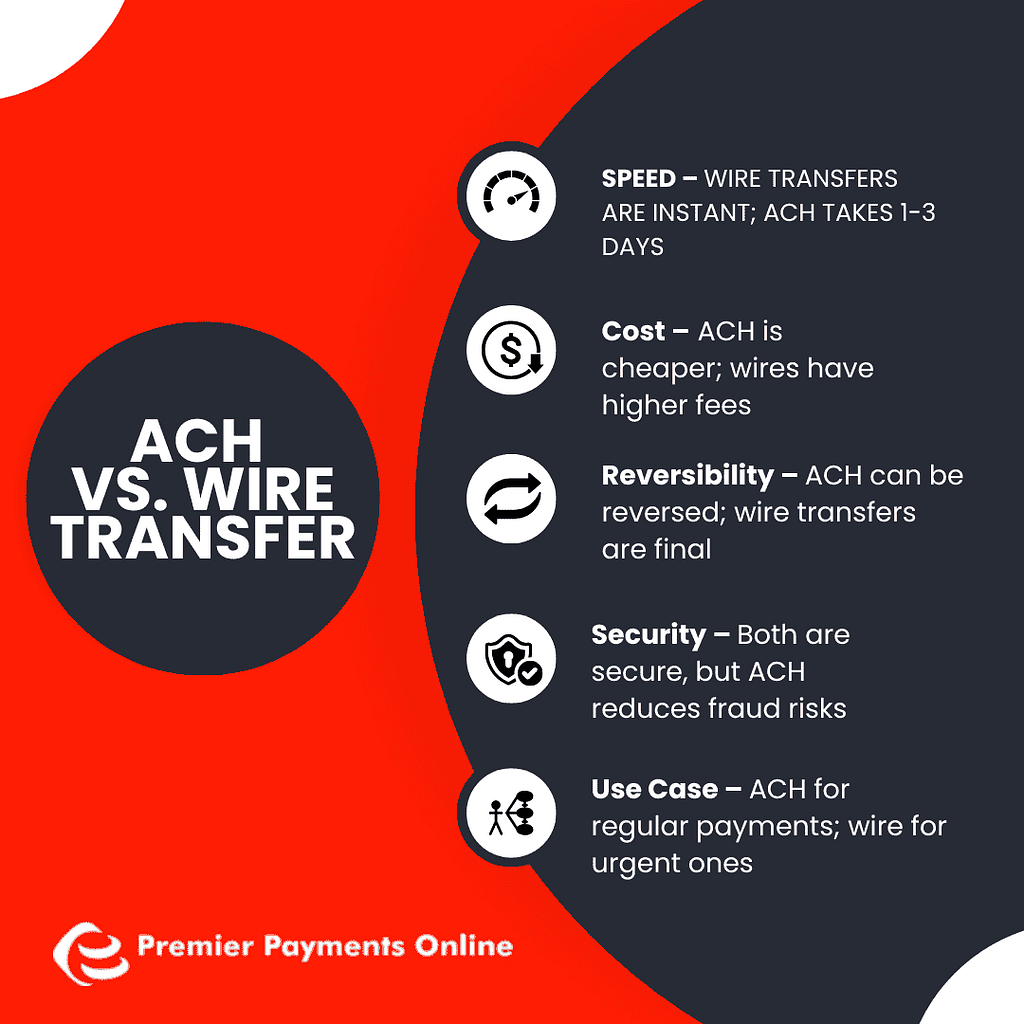
| Payment Method | Processing Time | Cost | Security | Tracking/Reconciliation Ease |
| ACH Payments | 1-3 days (same-day available) | Low (0.20−1.50 typical) | High (Nacha rules) | High (Electronic) |
| Wire Transfers | Same-day / Near real-time | High (15−50 typical) | High | Moderate |
| Credit Cards | Real-time authorization | Higher (Percentage + fixed fee) | High (PCI DSS) | Moderate |
| Paper Checks | 5-7+ days (mailing/clearing) | Moderate (Check stock, postage, labor) | Lower (Fraud risk) | Low (Manual) |
ACH payments often provide the best balance of cost-effectiveness, reliability, and ease of tracking for many types of business transactions. While other methods offer speed (wires) or consumer convenience (cards), the security standards for cards (PCI DSS) highlight the importance of compliance, something businesses should consider across all payment types. Understanding the benefits of PCI DSS compliance can inform security practices even for ACH payments.
9. Security Features in ACH Payments
The ACH payment network and its participants employ multiple layers of security inherent to the system itself:
| Security Feature | Description |
| Nacha Operating Rules | Comprehensive rulebook governing all participants, covering risk management and security standards for ACH payments. |
| Encryption | Data encryption is required during transmission and often at rest for sensitive account information related to ACH payments. |
| ODFI/RDFI Responsibilities | Banks have defined roles in verifying identities, monitoring fraud, and handling returns/disputes for ACH payments. |
| Authorization Requirements | Strict rules for obtaining and storing proof of authorization for ACH payment debits prevent unauthorized pulls. |
| Network Monitoring | ACH Operators and financial institutions use systems to monitor network activity for anomalies. |
These built-in features provide a secure foundation for ACH payments, but businesses must complement them with their security practices (detailed further in Section 13).
10. Implementing ACH Payments in Your Business
Follow these steps for a smooth ACH payment implementation:
- Assess Needs: Analyze your payment flows (payroll, vendor payments, customer collections) to determine volume and type of ACH payment transactions needed.
- Select Provider: Choose a bank or third-party processor that fits your volume, technical needs, and budget for ACH payments.
- Obtain Authorizations: Set up compliant processes to get authorization from employees (direct deposit) or customers (ACH payment debits).
- Integrate Systems: Connect the ACH payment processing solution with your accounting, ERP, or other business software.
- Establish Procedures: Define internal workflows for initiating, approving, and reconciling ACH payment transactions.
- Train Staff: Ensure relevant personnel understand the ACH payment process, tools, and compliance requirements (Nacha rules).
- Monitor & Reconcile: Implement regular monitoring of ACH payment transaction statuses and reconciliation against bank statements.
Working with experienced payment service providers like Premier Payments Online ensures your ACH payment implementation aligns with best practices and meets your specific business needs.
11. How ACH Payments Support Better Financial Decisions
Leveraging ACH payments and the associated data enables businesses to make more informed financial decisions:
| Insight Type | Business Benefit |
| Predictable Cash Flow | Improved working capital management and forecasting via scheduled ACH payments. |
| Optimized Payment Timing | Better vendor relationships, potential discounts through timely ACH payments. |
| Processing Efficiency | Reduced administrative overhead and labor costs associated with ACH payments. |
| Return/Reject Analysis | Lower error rates for ACH payments, improved data quality. |
| Payment Trend Analysis | Informed budgeting, resource allocation based on ACH payment data. |
By providing reliable, low-cost, and easily trackable electronic payments, the ACH payment network gives businesses data and tools for strategic financial planning and operational improvements.

12. Integrating ACH Payments into a Broader Strategy
While ACH Payment processing is powerful on its own, its true value often emerges when integrated into a comprehensive payment strategy. Businesses rarely rely on a single payment method. Effectively managing ACH payments alongside other options requires a cohesive approach, often leveraging technology for optimization.
- Omni-Channel Experience: Customers expect seamless payment experiences whether they are interacting online, in-store, or through other channels. Integrating ACH Payment options within an omni-channel framework ensures consistency and provides customers with preferred payment choices, including convenient billpay solutions.
- Payment Flow Optimization: Advanced systems can analyze transaction types, costs, and settlement times to route payments efficiently. This concept, sometimes involving intelligent payment routing, ensures that whether it’s an ACH Payment, card transaction, or other method, the most cost-effective and appropriate channel is used for each specific scenario, ultimately impacting how quickly a payment processed message is confirmed.
- Invoice and Billing Integration: Connecting ACH Payment capabilities directly with electronic invoice systems streamlines accounts receivable. This is particularly crucial for B2B transactions and can be scaled using robust invoice processing for enterprise solutions. Utilizing the top invoice processing for enterprises can significantly reduce manual effort and accelerate cash flow, especially when dealing with complex billing like understanding the benefits carrier invoice processing offers.
- Value-Added Services: Complementary services like gift, loyalty, and payroll cards can often be managed alongside core payment processing, including ACH Payment for funding payroll cards, offering a unified financial toolkit.
Integration Considerations:
| Aspect | Key Benefit | Potential Tool/Link |
| Unified Reporting | Single view across ACH Payment and other transaction types. | Payment Gateway Dashboards |
| Customer Experience | Consistent payment options across all touchpoints. | Omni-Channel Solutions |
| Efficiency | Automated routing and reconciliation reduce manual workload for ACH payments. | Integrated Accounting/ERP Software |
| Accounts Receivable | Faster payment collection via integrated invoicing and ACH Payment. | Electronic Invoice Systems |
13. Risk Management and Compliance for ACH Payments
The security features inherent in the ACH Payment network are robust, but businesses processing these transactions must also implement their own risk management and compliance practices. Handling bank account information requires diligence to protect data and maintain trust when dealing with ACH payments.
- Fraud Prevention: Implementing strong risk & fraud management protocols is essential for ACH payments. This includes verifying account ownership, monitoring for unusual transaction patterns, and adhering to Nacha rules regarding authorization and returns. Robust security helps prevent unauthorized ACH Payment debits.
- Data Security: While ACH Payment data falls under different regulations than credit cards (governed by PCI DSS), the principles of data protection are similar.
Securely storing and transmitting bank account numbers and routing information is critical. Adhering to high standards, similar to those required for PCI DSS, is best practice. Consider completing a PCI compliance test for card systems can highlight security weaknesses relevant to protecting ACH payment data too. Be mindful that failure to protect data can be costly, conceptually similar to incurring a PCI DSS non-compliance charge.
- Compliance Adherence: Staying compliant with Nacha Operating Rules is mandatory for participating in the ACH Payment network. Additionally, businesses should be aware of data privacy regulations and document their compliance efforts. This might involve internal reviews or processes similar to generating an attestation of compliance for other frameworks. Factor the resources needed for compliance, akin to calculating PCI DSS cost, into your operational planning.
Ensure secure data handling protocols are in place, understanding, for example, why sensitive data like account numbers shouldn’t be handled insecurely, drawing parallels from knowing if email files can be used as evidence for PCI.
Key Compliance & Risk Areas for ACH Payment
| Area | Focus | Importance |
| Authorization | Obtaining and storing proper consent for ACH Payment debits. | Prevents unauthorized transactions, ensures Nacha compliance. |
| Data Security | Protecting stored and transmitted bank account information for ACH payments. | Builds trust, prevents data breaches, and avoids reputational damage. |
| Returns Management | Handling returned ACH Payment transactions correctly (e.g., NSF). | Minimizes losses, maintains good standing within the ACH network. |
| Fraud Monitoring | Identifying and preventing suspicious ACH Payment activity. | Reduces financial losses and operational disruption. |
| Nacha Rule Updates | Staying informed about changes to the ACH Payment network rules. | Ensures ongoing compliance and avoids penalties. |
14. ACH Payments for Specialized Business Needs
The flexibility of the ACH Payment network makes it suitable for various specialized business models and industries, each potentially having unique requirements for managing their ACH payments:
- High-Risk Merchants: Businesses categorized as high-risk merchants often rely heavily on ACH Payment processing due to restrictions or higher costs associated with card payments. Robust fraud prevention and clear transaction descriptors are vital for their ACH payment activities.
- CPAs and Accountants: Professionals like CPAs use ACH payments for collecting client fees, processing payroll for clients, and managing trust accounts, requiring systems that handle multiple client funds securely via ACH payments.
- Resellers and Sales Organizations: Commercial resellers and career sales professionals often need reliable ACH Payment systems for collecting payments from end-customers or managing commission payouts efficiently using ACH payment.
- Brokers: Financial or other types of brokers may use ACH payments to facilitate fund movements between parties, requiring clear tracking and compliance adherence for all ACH payment transactions.
Businesses operating in these or other specialized areas should seek providers familiar with their unique challenges related to ACH payments. If you operate in such a niche, consider how you might partner with us to develop tailored ACH Payment solutions.
Streamline Your Payment Operations with Premier Payments Online
Understanding ACH payments is key to optimizing your financial operations. Premier Payments Online offers comprehensive payment solutions, including advanced ACH payment processing tailored to your business needs.
Our team of payment experts can help you implement a robust ACH payment system that integrates seamlessly with your existing financial infrastructure, providing clear visibility into all your electronic transactions while reducing costs and improving efficiency. We offer specialized programs, including our dedicated ACH & check acceptance program.
Contact Premier Payments Online today to learn how our ACH payment solutions can transform your operations with powerful management tools and industry-leading security.
Key Takeaways on ACH Payments
- ACH Payment is an electronic bank-to-bank transfer system in the U.S. governed by Nacha rules.
- It offers cost-effective, reliable, and automatable payment processing for businesses and individuals.
- ACH payments include credits (pushing funds) and debits (pulling funds), requiring proper authorization for debits.
- Processing times for ACH payments range from same-day to 3 business days.
- Implementing ACH payments provides significant benefits for cash flow management, reconciliation, and efficiency.
- Integration with other systems and strong risk management are crucial for maximizing the value and security of ACH payments.
- Security relies on both network rules and the business’s own data handling and compliance practices for ACH payments.











